
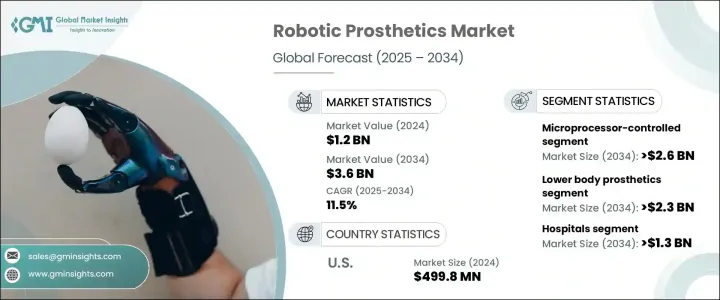
세계의 로봇 의족 시장은 2024년에는 12억 달러로 평가되었고, 의족 기술, 특히 로봇 용도의 진보와 이동 보조기 수요 증가로 인해 2034년에는 36억 달러에 달할 것으로 예측되며, CAGR 11.5%로 성장할 전망입니다.
인구 고령화, 외상, 당뇨병, 혈관 질환으로 인한 손실 사례의 증가와 같은 요인도 시장 확장을 촉진하고 있습니다.

로봇 의족, 특히 마이크로프로세서 제어(MPC) 및 AI 기반 모델은 향상된 기능과 적응성을 제공하여 사용자가 쉽게 움직일 수 있고 전반적인 삶의 질을 높입니다. 탄소 섬유 및 티타늄과 같은 경량 소재의 발전은 의족의 강도와 내구성을 크게 향상시키는 데 기여했습니다. 이러한 소재는 의족 장치의 전반적인 성능을 향상시킬 뿐만 아니라 의족을 더 편안하고 신뢰할 수 있으며 사용자 친화적으로 만듭니다. 이러한 재료의 사용은 강도를 저하시키지 않으면서 의족을 경량화하여 사용자가 자유롭게 움직일 수 있도록 합니다. 이는 기능성과 편안함을 모두 충족시키는 의족 솔루션을 찾는 사람들이 증가함에 따라 시장을 확대시키고 있습니다.
| 시장 범위 | |
|---|---|
| 시작 연도 | 2024년 |
| 예측 연도 | 2025-2034년 |
| 시작 금액 | 12억 달러 |
| 예측 금액 | 36억 달러 |
| CAGR | 11.5% |
시장은 기술 및 신체 부위 분류를 포함한 다양한 범주로 분류되며, 각 범주는 성장 촉진에 중요한 역할을 합니다. 예를 들어, 마이크로프로세서 제어(MPC) 의족 부문은 11.2%의 CAGR로 상당한 성장을 보일 것으로 예상됩니다. MPC 의족은 균형 개선, 에너지 관리 향상, 적응성 강화 등 다양한 장점을 제공합니다. 이러한 기능은 사용자가 더 자연스럽게 움직이고 독립성을 유지할 수 있도록 지원하며, 이는 고급 이동성 솔루션을 찾는 절단 환자들이 MPC 기술을 점점 더 선호하게 만들고 있습니다.
또 다른 중요한 부문인 하체 의족 시장은 11.4%의 CAGR로 강한 성장이 예상되며, 2034년까지 23억 달러에 달할 것으로 전망됩니다. 이 부문에는 사지 상실 후 움직임과 균형을 회복하는 데 필수적인 로봇 무릎과 발목이 포함됩니다. 이러한 의족 장치는 사용자의 보행, 달리기, 장시간 서 있는 능력을 향상시켜 전반적인 삶의 질을 크게 개선합니다. 하체 의족은 자율성과 이동성을 회복함으로써 개인이 더 활동적이고 충실한 삶을 영위할 수 있도록 돕습니다.
미국의 로봇 의족 시장은 2024년 4억 9,980만 달러로 평가되었으며, 이는 국가의 잘 구축된 의료 인프라와 상당한 의료 지출에 기인합니다. 미국은 사지 절단 환자 인구가 많아 고급 의족 기술에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있습니다. 국가의 연구 자금 지원과 의족 분야에서의 지속적인 기술 혁신은 미국을 글로벌 시장 리더로 자리매김하게 했으며, 이는 고품질 혁신적 로봇 의족 솔루션에 대한 수요를 더욱 촉진하고 있습니다.
Axile Bionics, Brain Robotics, Blachford Group 등 세계 로봇 의족 업계의 유력한 기업은 시장에서의 지위를 강화하기 위해 다양한 전략을 채택하고 있습니다. 예를 들어, Ottobock과 Fillauer LLC는 더 가벼우며 내구성이 뛰어난 의족 재료 개발을 위해 연구 개발에 투자하고 있습니다. 의료 전문가와의 협업과 정부 자금 지원은 Motorica와 Myomo와 같은 기업들이 제품을 개선하고 시장 점유율을 확대하는 데 기여했습니다. 또한 보험사 및 의료 기관과의 전략적 파트너십은 로봇 의족의 접근성을 확대해 필요로 하는 사람들에게 더 널리 제공되도록 돕고 있습니다.
The Global Robotic Prosthetics Market was valued at USD 1.2 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 11.5% to reach USD 3.6 billion by 2034, driven by advancements in prosthetic technology, especially robotic applications, and the increasing demand for mobility aids. Factors like an aging population, rising instances of loss due to trauma, diabetes, and vascular diseases are also fueling market expansion.
Robotic prosthetics, particularly microprocessor-controlled (MPC) and AI-driven models, offer improved functionality and adaptability, allowing users to move with ease and increasing the overall quality of life. The advancement of lightweight materials such as carbon fiber and titanium has significantly contributed to improving the strength and durability of prosthetics. These materials not only enhance the overall performance of prosthetic devices but also make them more comfortable, reliable, and user-friendly. The use of such materials ensures that the prosthetics are lightweight without compromising on strength, enabling users to move freely and with ease. This has expanded the market, as more individuals seek prosthetic solutions that cater to both functionality and comfort.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $1.2 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $3.6 Billion |
| CAGR | 11.5% |
The market is segmented into various categories, including technology and body part classifications, each playing a crucial role in driving growth. The microprocessor-controlled (MPC) prosthetics segment, for instance, is expected to witness considerable growth, with a projected CAGR of 11.2%. By 2034, this segment is anticipated to reach USD 2.6 billion in market value. MPC prosthetics offer substantial benefits, such as improved balance, better energy management, and enhanced adaptability. These features empower users to move more naturally and maintain greater independence, which makes MPC technology increasingly popular among amputees seeking advanced mobility solutions.
Another important segment, lower body prosthetics, is also set for strong growth, with a forecasted CAGR of 11.4%, reaching USD 2.3 billion by 2034, includes robotic knees and ankles, which play an essential role in restoring movement and balance following limb loss. These prosthetic devices are crucial for improving a user's ability to walk, run, and stand for longer periods, significantly enhancing their overall quality of life. By restoring autonomy and mobility, lower body prosthetics help individuals lead more active and fulfilling lives.
United States Robotic Prosthetics Market was valued at USD 499.8 million in 2024 due to the country's well-established healthcare infrastructure and substantial healthcare spending. The U.S. has a significant population of amputees, contributing to the rising demand for advanced prosthetic technologies. The nation's commitment to research funding and the continuous technological advancements in the field of prosthetics have positioned it as a global leader in the market. This has further fueled the demand for high-quality, innovative robotic prosthetic solutions.
Prominent players in the Global Robotic Prosthetics Industry, such as Axile Bionics, Brain Robotics, and Blatchford Group, are adopting various strategies to strengthen their market positions. These companies focus on continuous technological innovation, with an emphasis on improving the functionality, comfort, and affordability of robotic prosthetics. For instance, Ottobock and Fillauer LLC invest in R&D to develop lighter, more durable prosthetic materials. Collaborations with healthcare professionals and government funding have allowed companies like Motorica and Myomo to refine their products and expand their market share. Additionally, strategic partnerships with insurance providers and healthcare organizations are helping companies ensure wider accessibility of robotic prosthetics to those in need.