
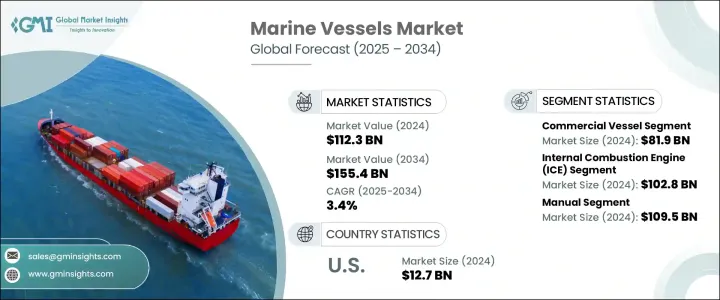
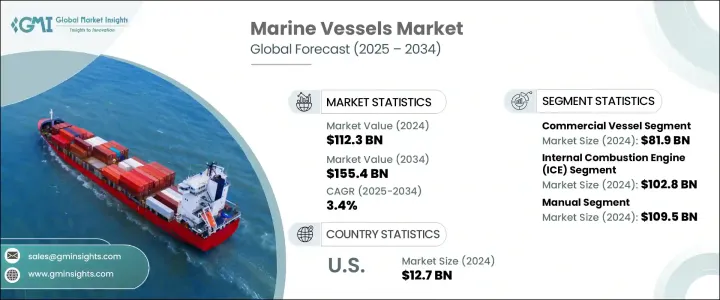
세계의 선박 시장은 2024년에 1,123억 달러로 평가되었고, 세계 해상 무역 규모 확대 및 해군 함대 근대화에 대한 정부 투자 증가로 CAGR 3.4%로 성장할 전망이며, 2034년에는 1,554억 달러에 이를 것으로 추정됩니다.
무역 루트가 확대되고 지정학적 긴장이 계속되는 가운데, 각국은 해군력을 강화고, 함대를 근대화하고 있으며, 상업선과 군용선 양쪽 모두에 안정된 수요를 낳고 있습니다. 해상 무역에서 물류 효율의 필요성은, 진화하는 해상 안전 보장 요건과 맞물려, 선진적인 선박에 대한 세계의 수요를 계속 형성하고 있습니다.
최근, 철강이나 알루미늄 등의 주요 수입 소재에 관세가 부과되어, 선박 업계 전체에 큰 파급 효과를 가져왔습니다. 이러한 정책은 국내 조선사의 제조 비용을 인상하고 미국에서 건조된 선박의 가격 경쟁력과 리드 타임을 국제적인 조선사보다 저하시켰습니다. 원재료비의 증가는 선박 건조의 진척을 늦추고 상업 계약이나 방위 계약의 예산을 압박했습니다. 더욱이 타국으로부터 부과된 보복 무역 조치로 인해 미국산 선박의 수출 가능성이 제한되어 국내 조선소의 조업상 및 재무상의 과제가 더욱 심화되었습니다. 이러한 정책으로 인해 초래된 불확실성은 공급망을 혼란스럽게 하고 프로젝트를 지연시키며 일부 조선사는 존속하기 위해 조달과 생산 전략을 재평가하도록 촉구되었습니다.
| 시장 범위 | |
|---|---|
| 시작 연도 | 2024년 |
| 예측 연도 | 2025-2034년 |
| 시작 금액 | 1,123억 달러 |
| 예측 금액 | 1,554억 달러 |
| CAGR | 3.4% |
상업선 부문은 2024년에 819억 달러로 평가되었습니다. 세계 해운 활동의 확대와 항만의 인프라 정비가 유조선, 컨테이너선, 장미 화물선을 늘릴 필요성을 부추기고 있습니다. 게다가 크루즈 여행의 부활과 대용량 페리 시스템의 도입이 이 부문의 성장을 뒷받침하고 있습니다. 몇몇 국가는 항만 및 해상 물류 네트워크에 대한 투자를 강화하고 있어 연안 및 내륙 수로의 특수선 및 피더선 수요를 더욱 높이고 있습니다.
추진력 기반에서는 내연 기관(ICE) 부문이 2024년에 1,028억 달러로 평가되었습니다. 이러한 엔진은 비용 효율성, 출력 신뢰성, 항속 거리 연장을 제공하며, 특히 장거리 화물 운송과 심해 작업에 매우 중요하기 때문에 업계에서는 정평이 많습니다. 많은 해운사와 오프쇼어 사업에 ICE 엔진 탑재선은 특히 연료 보급 인프라가 한정된 곳에서는 여전히 가장 현실적인 솔루션입니다. 이 추진력 유형은 해양 시추 및 물류 임무에서 대형선을 지원하는 능력도 있기 때문에 널리 채택되고 있습니다.
미국 선박 시장은 2024년에 127억 달러에 이르렀으며, 몇몇 견조한 수요 촉진요인에 의해 지원되고 있습니다. 특히 대규모 오프쇼어 에너지 프로젝트에서는, 특수한 서비스선 및 승무원 이송선의 요구가 확대되고 있어, 새로운 선박의 조달에 박차를 가하고 있습니다. 이러한 선박은, 해상 풍력 발전소나 에너지 플랫폼의 건설과 보수를 가능하게 하는데 있어서 중요한 역할을 하고 있습니다. 또한 내륙 수로 수송, 특히 하천 시스템의 활성화를 목표로 한 투자는 낡은 선대의 근대화를 촉진하고 지역 물류의 효율성과 지속 가능성을 향상시키고 있습니다.
세계 선박 업계의 주요 기업으로는 General Dynamics NASSCO, Vard, HII, Sumitomo Heavy Industries Marine and Engineering, Damen Shipyards Group, Meyer Werft, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Babcock International Group, Austal, SHI-MCI, Fincantieri, Meyer Turku, Navantia, Lurssen, Japan Marine United Corporation, Hyundai Heavy Industries, Tsuneishi Shipbuilding, Cochin Shipyard, Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers, 및 China Shipbuilding Industry Corporation 등이 있습니다.
시장의 타당성을 유지하고 세계적으로 확대하기 위해 주요 선박 제조업체는 차세대 선박 설계, 하이브리드 추진 시스템 통합, 고급 자동화 기술에 중점을 둡니다. 각 회사는 그린조선, LNG 추진, AI 주도의 유지보수 솔루션에 투자함으로써 탈탄소 목표에 전략을 맞추고 있습니다. 항만 당국, 해군, 로지스틱스 프로바이더와의 전략적 파트너십은 업무 범위를 확대하고, 적극적인 연구 개발 및 디지털 전환은 시장 리더를 경쟁사로부터 계속 차별화한다.
The Global Marine Vessels Market was valued at USD 112.3 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 3.4% to reach USD 155.4 billion by 2034, driven by the rising scale of global maritime trade and increasing government investments in naval fleet modernization. As trade routes expand and geopolitical tensions persist, countries are strengthening naval capabilities and modernizing their fleets, creating a stable demand for both commercial and military vessels. The need for logistical efficiency in seaborne trade, coupled with evolving maritime security requirements, continues to shape the global demand for advanced marine vessels.
The imposition of tariffs on key imported materials such as steel and aluminum in recent years created significant ripple effects across the marine vessels industry. These policies raised manufacturing costs for domestic shipbuilders, making U.S.-built vessels less competitive in pricing and lead times than their international counterparts. The increase in raw material expenses led to slower progress on vessel construction and strained budgets for commercial and defense contracts. Furthermore, retaliatory trade measures imposed by other nations restricted the export potential of American-built vessels, compounding the operational and financial challenges for domestic yards. The uncertainty introduced by such policies disrupted supply chains, delayed projects, and prompted some shipbuilders to reevaluate sourcing and production strategies to remain viable.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $112.3 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $155.4 Billion |
| CAGR | 3.4% |
The commercial vessels segment was valued at USD 81.9 billion in 2024. Expanding global shipping activities and infrastructure upgrades across ports fuel the need for more tankers, container ships, and bulk carriers. Additionally, the resurgence of cruise travel and the introduction of high-capacity ferry systems are helping drive segment growth. Several nations have stepped up investments in port and maritime logistics networks, which further amplifies the demand for specialized and feeder vessels across coastal and inland waterways.
On the basis of propulsion, the internal combustion engines (ICE) segment was valued at USD 102.8 billion in 2024. These engines are well-established in the industry, offering cost efficiency, power reliability, and extended range, especially crucial for long-haul cargo transport and deep-sea operations. For many shipping companies and offshore operations, ICE-powered ships remain the most practical solution, particularly where fueling infrastructure is limited. This propulsion type is also widely adopted for its ability to support heavy-duty vessels in offshore drilling and logistics missions.
United States Marine Vessels Market reached USD 12.7 billion in 2024, supported by several robust demand drivers. The expanding need for specialized service and crew transfer vessels, particularly for large-scale offshore energy projects, is fueling new vessel procurement. These vessels play a critical role in enabling the construction and maintenance of offshore wind farms and energy platforms. Additionally, investments aimed at revitalizing inland waterway transportation, especially across river systems, encourage the modernization of older fleets, improving efficiency and sustainability across regional logistics.
Key players in the Global Marine Vessels Industry include General Dynamics NASSCO, Vard, HII, Sumitomo Heavy Industries Marine and Engineering, Damen Shipyards Group, Meyer Werft, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Babcock International Group, Austal, SHI-MCI, Fincantieri, Meyer Turku, Navantia, Lurssen, Japan Marine United Corporation, Hyundai Heavy Industries, Tsuneishi Shipbuilding, Cochin Shipyard, Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers, and China Shipbuilding Industry Corporation.
To maintain market relevance and expand globally, leading marine vessel manufacturers focus on next-generation ship designs, integration of hybrid propulsion systems, and advanced automation technologies. Companies align their strategies with decarbonization goals by investing in green shipbuilding, LNG propulsion, and AI-driven maintenance solutions. Strategic partnerships with port authorities, naval forces, and logistics providers enhance operational reach, while aggressive R&D and digital transformation continue to differentiate market leaders from competitors.