
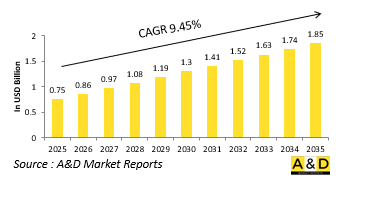
전 세계 수중 스웜전 시장 규모는 2025년에 약 7억 5,000만 달러로 추정되며, 2035년에는 18억 5,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예상되며, 예측 기간인 2025-2035년 동안 9.45%의 CAGR로 성장할 것으로 예상됩니다.
자율 시스템, 통신 프로토콜, 수중 추진의 발전으로 수중 스웜전 능력의 개발이 크게 가속화되고 있습니다. 이러한 진화의 핵심은 AI의 활용으로, 수중 드론이 인간의 직접적인 통제 없이도 협업할 수 있게 해줍니다. 이러한 시스템은 분산형 의사결정 모델을 사용하여 각 유닛이 센서 데이터를 처리하고 역동적인 시나리오에 집단적으로 대응할 수 있도록 합니다. 수중 통신에는 고유한 문제가 있지만, 최근 음향 신호 및 광 데이터 전송의 혁신으로 인해 군집 구성원 간의 실시간 협력이 향상되었습니다. 센서의 소형화와 에너지 효율의 향상으로 소형 차량이 더 오래 작동하고 복잡한 수중 지형을 항해할 수 있게 되었습니다. 기계 학습 알고리즘은 경로 계획, 위협 식별, 적응형 작전 수행을 정교화하여 감시, 지역 제압 또는 협동 공격의 역할에서 스웜을 더욱 효과적으로 만들 수 있도록 돕습니다. 스웜 시스템은 소나 매핑, 페이로드 전달, 전자전 등의 임무에 맞는 페이로드를 탑재할 수 있는 모듈성 또한 장점입니다. 이중화도 기술적 강점이며, 한 유닛이 고장나거나 무력화되어도 다른 유닛이 원활하게 적응하여 작전의 연속성을 유지합니다. 이러한 기술 혁신으로 인해 해저전투는 경직된 집중형 작전에서 유연하고 지능적인 작전으로 전환되고 있습니다. 그 결과, 위협과 기회에 실시간으로 적응할 수 있는 탄력적인 수중 네트워크가 구축되어 해군의 수중 작전을 근본적으로 변화시킬 것입니다.
수중 스웜전의 모멘텀은 전략적, 작전적, 기술적 요구의 수렴에 의해 촉진되고 있습니다. 주요 촉진요인 중 하나는 적대세력이 스텔스 플랫폼, 무인 시스템, 비관습적 전술을 채택하는 수중 환경의 복잡성이 증가하고 있다는 점입니다. 군집 기반 접근 방식은 광활한 해양 공간에서 지속적이고 분산된 감시와 신속한 대응 능력을 제공함으로써 효과적인 대응책을 제공합니다. 또한, 기존의 유인 잠수정과 수상정의 높은 비용과 취약성으로 인해, 특히 위험도가 높거나 자원 집약적인 작전에서는 군집은 매력적인 보완 및 대안이 될 수 있습니다. 특히 분쟁이 끊이지 않는 해역에서 해상의 우위를 유지하려는 전략적 욕구는 해군을 유연하게 다수 배치할 수 있는 확장 가능한 솔루션을 추구하도록 유도하고 있습니다. 운용 측면에서, 스웜은 인원의 위험을 증가시키지 않고 상황 인식과 전력 투사를 강화하기 때문에 정찰, 기뢰 대응, 전자 교란 작전에 이상적입니다. 개발 측면에서는 AUV와 오픈 소스 내비게이션 시스템을 저렴한 가격에 이용할 수 있게 됨에 따라 더 많은 국가들이 군집 기술을 탐색할 수 있게 되었습니다. 실시간 인텔리전스, 네트워크화된 전쟁, 적응형 작전 수행에 대한 중요성이 강조되면서 그 매력은 더욱 강조되고 있습니다. 그 결과, 전략적 억제력, 작전의 다양성, 기술적 실현 가능성의 조합으로 인해 수중 소용돌이는 미래 해양 방어 정책의 중요한 구성요소로 자리 잡고 있습니다.
수중 스웜전에 대한 각 지역의 접근 방식은 다양한 전략적 관심사, 기술적 역량, 해양에서의 우선순위를 반영합니다. 아시아태평양에서는 긴장 고조와 영토 분쟁으로 인해 자율 수중 기술에 대한 투자가 급증하고 있습니다. 광활한 해안선을 보유하고 해양에 대한 적극적인 영유권을 주장하는 국가들은 수중 감시와 침입 방지를 강화하기 위해 스웜 능력을 모색하고 있습니다.
세계의 수중 스웜전 시장에 대해 조사 분석했으며, 성장 촉진요인, 향후 10년간의 시장 전망, 각 지역별 동향 등의 정보를 전해드립니다.
지역별
동작 방식별
추진별
북미
촉진요인, 억제요인, 과제
PEST
주요 기업
공급업체 Tier 상황
기업 벤치마크
유럽
중동
아시아태평양
남미
미국
방위 프로그램
최신 뉴스
특허
이 시장의 현재 기술 성숙도
캐나다
이탈리아
프랑스
독일
네덜란드
벨기에
스페인
스웨덴
그리스
호주
남아프리카공화국
인도
중국
러시아
한국
일본
말레이시아
싱가포르
브라질
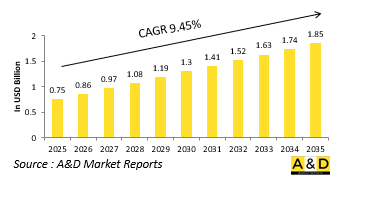
The Global Underwater Swarm Warfare market is estimated at USD 0.75 billion in 2025, projected to grow to USD 1.85 billion by 2035 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 9.45% over the forecast period 2025-2035.
Underwater swarm warfare is emerging as a transformative concept in naval defense, characterized by the coordinated use of multiple autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) to achieve strategic and tactical objectives. These swarms operate as decentralized, intelligent networks capable of executing complex missions with minimal human oversight. Unlike traditional underwater systems that rely on singular, high-value assets, swarm-based strategies emphasize redundancy, adaptability, and coverage. This paradigm enables navies to conduct reconnaissance, surveillance, mine detection, and offensive operations simultaneously across large maritime areas. The core advantage lies in the swarm's collective behavior, where individual units share information in real-time to respond dynamically to threats, obstacles, or environmental changes. As maritime zones grow increasingly contested and adversaries adopt stealthier undersea tactics, the need for persistent and reactive underwater presence becomes critical. Swarm warfare introduces a new layer of deterrence by overwhelming enemy defenses, complicating targeting decisions, and enhancing domain awareness. Global interest in this capability is rising, with militaries investing in research and prototyping to harness its full potential. As the underwater domain becomes a theater of greater strategic competition, swarm warfare is set to play a pivotal role in shaping future naval engagements, offering a blend of autonomy, scalability, and resilience that traditional systems cannot match.
Advances in autonomous systems, communication protocols, and underwater propulsion have significantly accelerated the development of underwater swarm warfare capabilities. Central to this evolution is the application of artificial intelligence, enabling underwater drones to operate collaboratively without direct human control. These systems use decentralized decision-making models, allowing each unit to process sensor data and respond collectively to dynamic scenarios. Communication underwater presents unique challenges, and recent innovations in acoustic signaling and optical data transfer have improved real-time coordination among swarm members. Sensor miniaturization and improved energy efficiency allow for smaller vehicles that can operate longer and navigate complex underwater terrains. Machine learning algorithms help refine path planning, threat identification, and adaptive mission execution, making swarms more effective in surveillance, area denial, or coordinated attack roles. Swarm systems also benefit from modularity, with payloads tailored for tasks like sonar mapping, payload delivery, or electronic warfare. Redundancy is another technological strength-if one unit fails or is neutralized, others seamlessly adapt to maintain mission continuity. Collectively, these innovations are shifting undersea warfare from rigid, centralized operations to flexible, intelligent engagements. The result is a resilient underwater network capable of adjusting in real-time to threats and opportunities, fundamentally changing how naval forces operate beneath the surface.
The momentum behind underwater swarm warfare is being driven by a convergence of strategic, operational, and technological imperatives. One of the primary motivators is the growing complexity of undersea environments, where adversaries increasingly employ stealthy platforms, unmanned systems, and unconventional tactics. Swarm-based approaches provide an effective counter by offering persistent, distributed surveillance and rapid response capabilities across broad ocean spaces. Additionally, the high cost and vulnerability of traditional manned submarines and surface ships make swarms an attractive supplement or alternative, especially for high-risk or resource-intensive missions. The strategic desire to maintain undersea dominance, particularly in contested maritime zones, is pushing navies to seek scalable solutions that can be deployed flexibly and in large numbers. Operationally, swarms enhance situational awareness and force projection without escalating risk to personnel, making them ideal for reconnaissance, mine countermeasures, and electronic disruption tasks. From a development standpoint, the increasing affordability of autonomous underwater vehicles and open-source navigation systems is enabling more countries to explore swarm technologies. The emphasis on real-time intelligence, networked warfare, and adaptive mission execution further underscores the appeal. Ultimately, the combination of strategic deterrence, operational versatility, and technological feasibility positions underwater swarms as a key component in future naval defense doctrines.
Regional approaches to underwater swarm warfare reflect a range of strategic interests, technological capacities, and maritime priorities. In the Asia-Pacific, rising tensions and territorial disputes have prompted a surge in investment in autonomous underwater technologies. Countries with large coastlines and active maritime claims are exploring swarm capabilities to enhance underwater surveillance and counter-intrusion measures. North American defense initiatives, particularly those led by the United States, are focusing on integrating swarms into broader multi-domain strategies, emphasizing interoperability and long-range mission capabilities. These efforts include experimentation with autonomous swarms as force multipliers in complex undersea environments. In Europe, collaborative defense projects are developing scalable swarm systems tailored for littoral defense, port protection, and anti-submarine operations, with a strong emphasis on interoperability among NATO allies. Middle Eastern navies are increasingly interested in undersea swarms for coastal monitoring and infrastructure protection, particularly around chokepoints and strategic waterways. In Latin America and Africa, while adoption is in earlier stages, interest is growing in using underwater swarms for anti-smuggling, illegal fishing deterrence, and maritime resource protection. Across all regions, there is a growing recognition that underwater swarm warfare offers a low-risk, high-impact method of securing maritime interests, especially as near-peer competition and asymmetric threats continue to evolve in the underwater domain.
German Company Deploys Underwater Spy Drone Swarm That Can Operate Stealthily for 3 Months, Marking a Major Maritime Breakthrough. Amid rising concerns over underwater security, an innovative German firm has introduced the SG-1 Fathom-an advanced autonomous underwater glider designed to patrol the ocean's depths for up to three months at a time. This cutting-edge technology is set to transform maritime surveillance and reshape the landscape of underwater threat detection.
By Region
By Mode Of Operation
By Propulsion
The 10-year underwater swarm warfare market analysis would give a detailed overview of underwater swarm warfare market growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
The 10-year underwater swarm warfare market forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
The regional underwater swarm warfare market trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.