
전 세계 무인 헬리콥터 시장 규모는 2025년에 21억 5,000만 달러로 추정되며, 2035년에는 189억 2,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예상되며, 예측 기간인 2025-2035년 동안 24.29%의 연평균 성장률을 보일 것으로 예상됩니다.
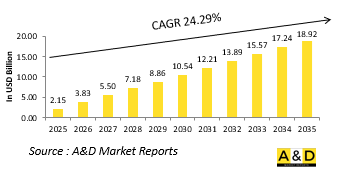
기술의 급속한 발전으로 국방용 무인 헬리콥터의 능력과 작전 프로필이 크게 향상되었습니다. 자율 항법, 센서 융합, 온보드 컴퓨팅의 혁신은 이러한 플랫폼이 역동적인 전투 환경에서 효과적으로 활동할 수 있게 해줍니다. 전장의 데이터를 실시간으로 처리하고 반응할 수 있어 운영자의 부담을 줄이고 보다 복잡한 작전을 수행할 수 있습니다. 고해상도 이미징 시스템, 합성개구부 레이더, 전자전 페이로드는 상황 인식과 위협 탐지를 강화하는 표준 기능이 되었으며, AI는 무인 헬리콥터의 위협 예측 분석과 자율적인 목표 추적을 가능하게 하는 등 의사결정 능력을 혁신적으로 변화시키고 있습니다. 보안 통신 링크는 신호 간섭이 심한 환경에서도 사령부 및 다른 군사 자산과의 연계를 보장합니다. 또한, 에너지 효율적인 추진 시스템은 비행 시간을 연장하고 스텔스 작전에 필수적인 정숙성을 향상시키는 데 기여합니다. 다른 무인 및 유인 시스템과의 상호운용성도 우선순위가 높으며, 통합군 작전 및 통합방위전략을 지원합니다. 모듈식 아키텍처는 신속한 페이로드 교체가 가능하여 정찰에서 전술적 보급에 이르기까지 다양한 작전에 헬리콥터를 맞출 수 있습니다. 전반적으로, 기술의 발전으로 국방용 무인 헬리콥터는 다양한 전투 조건에서 능력을 발휘할 수 있는 적응형 플랫폼으로 변화하고 있으며, 동시에 인명 위험을 줄이고 전략적 도달 범위를 확장하고 있습니다.
여러 가지 요인이 전 세계적으로 국방 분야에서 무인 헬리콥터의 채택과 발전을 촉진하고 있습니다. 가장 중요한 것은 위험도가 높은 작전에서 인력을 제거하여 사상자를 줄여야 할 필요성입니다. 무인 헬리콥터는 전방 정찰, 적진 수색 및 구조, 전쟁터에서의 병참 지원과 같은 작전에 신뢰할 수 있는 솔루션을 제공합니다. 복잡해지는 현대전에서는 신속하고 유연한 대응 메커니즘이 필요하며, 이러한 항공 플랫폼은 이를 실현하는 데 적합합니다. 지정학적 긴장과 영토 분쟁으로 인해 각국은 감시 및 정보 수집 능력을 강화해야 하며, 이는 종종 유인 항공기가 제한을 받는 환경에서 이루어집니다. 예산의 제약과 운영 효율성에 대한 요구는 군사 계획가들이 유지보수 및 인력 감축을 통해 장기적인 비용 우위를 제공하는 플랫폼으로 향하게 하고 있습니다. 또한, 네트워크 중심의 전쟁이 강조되면서 무인 헬리콥터의 실시간 데이터 공유 능력은 특히 중요하게 여겨지고 있습니다. 전 세계의 국방 현대화 프로그램은 기존 자산을 보완하고 전장에서의 인지도를 높이기 위해 무인 시스템 통합을 우선순위에 두고 있습니다. 환경 적응성, 스텔스 기능, 육상/해상 작전과의 호환성은 무인 시스템의 매력을 더욱 높여주고 있습니다. 이러한 촉진요인이 집약됨에 따라 국방 전략에서 무인 헬리콥터의 역할은 계속 확대되고 있으며, 현대 군사 작전에 필수적인 도구가 되고 있습니다.
국방용 무인 헬리콥터의 개발 및 배치는 지역마다 다른 패턴을 보이고 있으며, 각 지역의 전략적 우선순위와 안보 상황에 따라 형성되고 있습니다. 북미, 특히 미국에서는 기존 전력 구조와 원활하게 통합될 수 있는 다중 임무 자율 플랫폼을 구축하기 위해 많은 투자가 이루어지고 있습니다. 상호운용성, 내구성, 첨단 페이로드 능력에 중점을 두고 있습니다. 유럽에서는 각국이 감시, 국경 보안 및 즉각적인 대응 작전을 강화하기 위한 공동 개발 프로그램에 집중하고 있습니다. 이러한 노력은 비용과 전문 지식을 공유하기 위해 국내 기업과 국제적인 방위 파트너가 협력하는 경우가 많습니다.
세계의 무인 헬리콥터 시장에 대해 조사 분석했으며, 성장 촉진요인, 향후 10년간의 시장 전망, 지역별 동향 등의 정보를 전해드립니다.
최종사용자별
지역별
페이로드별
북미
촉진요인, 억제요인, 과제
PEST
주요 기업
공급업체 Tier 상황
기업 벤치마크
유럽
중동
아시아태평양
남미
미국
방위 프로그램
최신 뉴스
특허
이 시장의 현재 기술 성숙도
캐나다
이탈리아
프랑스
독일
네덜란드
벨기에
스페인
스웨덴
그리스
호주
남아프리카공화국
인도
중국
러시아
한국
일본
말레이시아
싱가포르
브라질
The global Unmanned Helicopter market is estimated at USD 2.15 billion in 2025, projected to grow to USD 18.92 billion by 2035 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 24.29% over the forecast period 2025-2035.
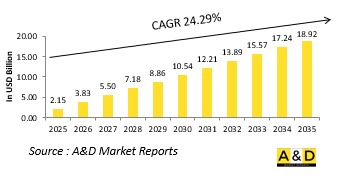
Defense unmanned helicopters are emerging as critical assets in modern military operations due to their ability to conduct missions without risking human life. These systems combine the agility of rotary-wing aircraft with the benefits of autonomy or remote operation, making them well-suited for reconnaissance, target acquisition, logistics, and electronic warfare. Their ability to hover and operate in confined or hostile environments gives military planners greater flexibility compared to traditional aerial platforms. As the nature of warfare evolves, defense forces around the world are increasingly prioritizing systems that can provide persistent surveillance, quick response, and low observable profiles. Unmanned helicopters are particularly valuable in missions that require quiet operation, rapid deployment, and access to complex terrains. Militaries globally are investing in both the development of indigenous platforms and the acquisition of advanced models from established defense contractors. These systems are being integrated into broader defense networks, working in tandem with ground forces, satellites, and other aerial vehicles. Their modular design allows customization based on mission requirements, which enhances their versatility. In an era of asymmetric threats and contested airspaces, the global interest in defense unmanned helicopters continues to grow, reflecting their strategic importance in achieving operational superiority without direct human involvement.
The rapid evolution of technology has significantly enhanced the capabilities and mission profiles of defense unmanned helicopters. Innovations in autonomous navigation, sensor fusion, and onboard computing allow these platforms to operate effectively in dynamic combat environments. They can process and react to battlefield data in real time, reducing the burden on operators and enabling more complex missions. High-resolution imaging systems, synthetic aperture radars, and electronic warfare payloads are now standard features, enhancing situational awareness and threat detection. Artificial intelligence is transforming decision-making capabilities, enabling unmanned helicopters to conduct predictive threat analysis and autonomous target tracking. Secure communication links ensure coordination with command centers and other military assets, even in environments with heavy signal interference. Furthermore, energy-efficient propulsion systems contribute to extended flight durations and quieter operation, which is crucial for stealth missions. Interoperability with other unmanned and manned systems has also become a priority, supporting joint-force operations and integrated defense strategies. Modular architectures allow rapid payload swapping, tailoring the helicopter for missions ranging from surveillance to tactical resupply. Overall, technological advancements are turning defense unmanned helicopters into highly adaptive platforms that can perform under diverse combat conditions while reducing risk to human personnel and increasing strategic reach.
Several key factors are fueling the global adoption and advancement of unmanned helicopters within defense sectors. Foremost among these is the need to reduce casualties by removing personnel from high-risk missions. Unmanned helicopters provide a reliable solution for tasks such as forward reconnaissance, search and rescue in hostile zones, and logistics support under fire. The increasing complexity of modern warfare demands rapid and flexible response mechanisms, which these aerial platforms are well-suited to deliver. Geopolitical tensions and territorial disputes are prompting nations to strengthen surveillance and intelligence-gathering capabilities, often in environments where manned aircraft face limitations. Budget constraints and the demand for operational efficiency are also pushing military planners toward platforms that offer long-term cost advantages through reduced maintenance and personnel requirements. Additionally, the growing emphasis on network-centric warfare makes the real-time data-sharing capabilities of unmanned helicopters particularly valuable. Defense modernization programs worldwide are prioritizing the integration of unmanned systems to complement traditional assets and enhance battlefield awareness. Environmental adaptability, stealth features, and compatibility with land and naval operations further amplify their appeal. As these drivers converge, the role of unmanned helicopters in defense strategy continues to expand, making them essential tools for modern military operations.
Different regions are exhibiting distinct patterns in the development and deployment of defense unmanned helicopters, shaped by their strategic priorities and security landscapes. In North America, particularly within the United States, significant investment is directed toward creating multi-mission autonomous platforms that can seamlessly integrate with existing force structures. Emphasis is placed on interoperability, endurance, and advanced payload capabilities. In Europe, nations are focusing on joint development programs aimed at enhancing surveillance, border security, and rapid-response operations. These efforts often involve collaborations between domestic firms and international defense partners to share costs and expertise. Asia-Pacific countries are rapidly expanding their defense capabilities, with unmanned helicopters seen as a critical component for maritime security, territorial monitoring, and asymmetric threat deterrence. Nations with large coastlines or contested borders are especially focused on systems that provide persistent aerial presence. In the Middle East, concerns about insurgency and border infiltration are driving demand for unmanned platforms that can conduct surveillance and precision targeting in harsh environments. Meanwhile, Latin America and Africa are gradually exploring these technologies, often through partnerships or procurement from established producers. Across all regions, the underlying trend is a growing recognition of the value unmanned helicopters bring to modern, tech-enabled defense strategies.
Dutch unmanned helicopter systems specialist High Eye announced it had secured a contract from the Netherlands Ministry of Defence (MoD) to supply its Airboxer vertical take-off and landing unmanned aerial vehicle (VTOL UAV). The contract was awarded through an open international tender, according to High Eye. While the company did not disclose the number of UAVs ordered or the contract's value, it confirmed that the first unit will be delivered within the year. The Airboxer VTOL UAV features a traditional helicopter configuration with a main and tail rotor and is powered by an air-cooled boxer engine with fuel injection. It can carry a variety of payloads, sensors, and other equipment weighing up to 7 kg. At sea level, the UAV can carry a 7 kg payload for several hours. With a 2 kg payload, it can sustain flight for more than three hours at a cruising speed of 30 knots (55.6 km/h) and reach speeds of up to 70 knots. The aircraft's maximum take-off weight at sea level is 32 kg, which gradually decreases with altitude up to its service ceiling of 10,000 ft (approximately 3,048 meters).
By End User
By Region
By Payload
The 10-year unmanned helicopter market analysis would give a detailed overview of unmanned helicopter market growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
The 10-year unmanned helicopter market forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
The regional unmanned helicopter market trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.