
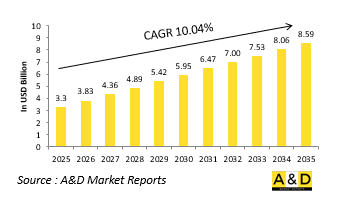
세계의 자세 시험 시장 규모는 2025년 33억 달러에서 예측 기간 중 10.04%의 CAGR로 추이하며, 2035년에는 85억 9,000만 달러로 성장할 것으로 예측됩니다.
세계 방산 부문에서의 자세 시험은 플랫폼의 자세 제어 및 안정성 시스템이 동적 운용 조건에서 제대로 작동하는지 평가 및 검증하는 과정을 말합니다. 여기서 자세란 우주 공간에서 물체의 방향을 의미하며, 일반적으로 피치, 롤, 요의 세 축을 기준으로 지구나 관성 좌표계와 같은 기준 프레임에 대해 정의됩니다. 국방 분야에서는 유도 미사일, 우주선, 무인 항공기(UAV), 전투기, 위성 시스템 등 다양한 플랫폼에서 정밀한 자세 제어가 필수적입니다. 자세 시험은 이러한 플랫폼이 실시간 제약 조건에서도 항법, 조준, 임무 수행을 위해 정확하게 자세를 유지하거나 조정할 수 있는지를 보장합니다. 예를 들어 요격 미사일은 비행 중 자세를 정확하게 조정하여 이동 목표물을 명중시켜야 하고, 정찰용 드론은 바람과 같은 외란에도 자세를 안정적으로 유지하여 고정밀 영상을 획득해야 합니다. 마찬가지로 인공위성이나 우주배치형 방위자산은 정지궤도 유지와 지구관측 및 통신을 위한 재방향 조정에 있으며, 견고한 자세 제어가 요구됩니다. 자세시험은 관성측정장비(IMU), 자이로스코프, 가속도계, 자력계, 통합 비행제어시스템의 신뢰성을 시뮬레이션 환경과 실제 환경 모두에서 검증합니다. 이를 통해 다양한 플랫폼이 정해진 성능 및 안전 기준을 충족할 수 있는 기반을 제공합니다.
기술의 발전으로 방위산업 분야의 자세 시험 능력과 정확도가 비약적으로 향상되고 있습니다. 오늘날의 첨단 자세 시험 시설에서는 실제 항법 및 제어 하드웨어를 사용하면서 비행 동역학 및 제어 피드백을 실시간으로 시뮬레이션할 수 있는 HIL(Hardware-in-the-Loop) 시스템을 도입하고 있습니다. 이를 통해 개발자는 복잡한 운영 시나리오를 재현한 제어 환경에서 제어 알고리즘, 응답 거동, 오차 보정 기능을 검증할 수 있습니다. 특히 MEMS 기반 자이로스코프, 가속도계 등 센서의 소형화를 통해 마이크로 UAV 및 소형 위성을 위한 소형이지만 고성능의 자세 제어 시스템을 시험할 수 있습니다. 또한 6자유도(6-DOF) 모션 플랫폼과 다축 속도 테이블을 활용하여 각도 이동, 가속도, 회전 등 모든 방향의 운동을 시뮬레이션함으로써 국방 엔지니어는 동적 하중과 진동, 다축 기동 중 자세 제어 메커니즘을 평가할 수 있게 되었습니다. 평가할 수 있습니다. 또한 AI 분석 및 디지털 신호 처리 툴의 도입으로 센서의 드리프트, 지연, 제어 정확도 등의 요소를 이전보다 훨씬 더 세밀하게 분석할 수 있게 되었습니다. 소프트웨어 정의 비행 제어 로직이 통합되어 테스트 파라미터를 실시간으로 재구성할 수 있는 적응형 테스트 환경도 구현되어 한계 조건과 시스템 작동 한계를 유연하게 검증할 수 있습니다. 또한 광학 및 자기식 자세 센서의 발전으로 위성 자세 테스트도 혜택을 받고 있으며, 궤도에서의 거동을 지상에서 정밀하게 시뮬레이션하고 검증할 수 있게 되었습니다. 이러한 기술 혁신은 시험의 정확도를 향상시켰을 뿐만 아니라, 피드백 루프의 속도를 높여 복잡한 자세 제어 시스템의 반복 개발 및 조기 결함 감지가 가능해졌습니다.
현대전의 전략적, 작전적 요구로 인해 자세 시험의 중요성이 비약적으로 증가하여 국방 분야의 주요 투자 및 개발 영역이 되었습니다. 주요 추진 요인 중 하나는 자율 및 반자율 시스템 증가입니다. 이러한 시스템은 역동적이고 적대적인 환경에서 독립적으로 작동하기 위해 첨단 정밀한 자세 제어에 크게 의존하고 있습니다. 예를 들어 무인항공기(UAV), 순항미사일, 배회형 무기 등은 안정적인 비행경로 유지, 신속한 방향전환, 임무 매개변수 변경에 대한 대응 등의 기능을 수행해야 하며, 이를 실현하기 위해서는 사전에 엄격한 자세제어시스템의 테스트가 필수적입니다. 또 다른 큰 요인은 멀티 도메인 작전의 부상입니다. 항공, 해상, 육상, 우주, 사이버 등 여러 영역에서 통합적인 임무를 수행하기 위해서는 항법 및 표적 시스템 간의 원활한 상호 운용성이 필수적이며, 이를 위해서는 조화로운 자세 데이터 통합이 기반이 됩니다. 또한 극초음속 무기와 우주 배치형 무기의 보급도 복잡성을 증가시키고 있습니다. 이러한 시스템에서는 고속 기동과 미세 중력 환경에서의 자세 제어가 요구되므로 기존과는 다른 첨단 시험 요구사항이 발생하고 있습니다. 또한 국방부 및 각국의 군 기관은 안전 및 성능에 대한 엄격한 규정을 부과하고 있으며, 시스템 인증 및 수용 시험의 일환으로 종합적인 자세 시험을 의무화하고 있습니다. 또한 민수/군 이중 사용 기술에 대한 수출 규제 또한 국제 표준 또는 제3자에 의한 엄격한 자세 성능 검증을 요구하는 경우가 많아지고 있습니다. 그리고 재밍(방해), 스푸핑(스푸핑), 전자 간섭과 같은 위협이 증가함에 따라 개발자들은 열악한 환경에서 자세 제어 시스템의 스트레스 테스트를 실시하여 작전상 복원력을 확보해야 합니다.
세계의 방위 부문용 자세 시험 시장을 조사했으며, 시장의 현황, 기술 동향, 시장 영향요인의 분석, 시장 규모 추이·예측, 지역별 상세 분석, 경쟁 구도, 주요 기업의 개요 등을 정리하여 전해드립니다.
지역별
유형별
플랫폼별
컴포넌트별
북미
촉진요인, 제약, 과제
억제요인
주요 기업
공급업체 Tier의 상황
기업 벤치마킹
유럽
중동
아시아태평양
남미
미국
방위 프로그램
최신 뉴스
특허
현재 기술 성숙도
캐나다
이탈리아
프랑스
독일
네덜란드
벨기에
스페인
스웨덴
그리스
호주
남아프리카공화국
인도
중국
러시아
한국
일본
말레이시아
싱가포르
브라질
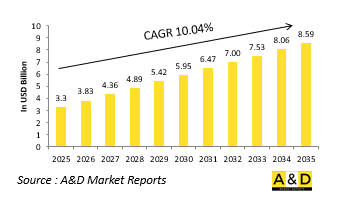
The Global Attitude Testing Market is estimated at USD 3.30 billion in 2025, projected to grow to USD 8.59 billion by 2035 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 10.04% over the forecast period 2025-2035.
Attitude testing in the global defense sector refers to the evaluation and validation of a platform's orientation control and stability systems under dynamic operating conditions. Attitude, in this context, denotes the orientation of an object in space-typically expressed in terms of pitch, roll, and yaw-relative to a reference frame, such as Earth or another inertial coordinate system. In defense, precise control of attitude is critical across a wide array of platforms, including guided missiles, spacecraft, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), fighter aircraft, and satellite systems. Attitude testing ensures that these platforms can maintain or adjust their orientation to fulfill navigational, targeting, and operational missions under real-time constraints. For instance, an interceptor missile must accurately adjust its trajectory mid-flight to engage a moving target, while a reconnaissance drone must stabilize its orientation despite wind disturbances to capture high-fidelity imagery. Likewise, satellites and space-based defense assets require robust attitude control to maintain geostationary positions or realign for Earth observation or communication. Attitude testing verifies the reliability of inertial measurement units (IMUs), gyroscopes, accelerometers, magnetometers, and integrated flight control systems under both simulated and real-world conditions, providing a baseline for performance and safety certification across domains.
Technology has dramatically elevated the capabilities and precision of attitude testing in defense applications. Modern attitude testing facilities now incorporate hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) systems, enabling real-time simulation of flight dynamics and control feedback with actual navigation and control hardware. This allows developers to validate control algorithms, response behavior, and error correction in a controlled environment that replicates complex operational scenarios. Miniaturization of sensors-especially MEMS-based gyroscopes and accelerometers-has facilitated the testing of compact yet powerful attitude control systems, especially for micro-UAVs and small satellites. Additionally, six-degree-of-freedom (6-DOF) motion platforms and multi-axis rate tables are increasingly used to simulate full-range angular movement, acceleration, and rotation, enabling defense engineers to test attitude control mechanisms under dynamic loads, vibrations, and multi-axis maneuvers. AI-enabled analytics and digital signal processing tools are being deployed to analyze sensor drift, latency, and control accuracy with unprecedented granularity. Moreover, the integration of software-defined flight control logic allows for adaptive testing environments, where test parameters can be reconfigured in real-time to explore boundary conditions and system limits. Satellite attitude testing has also benefitted from advancements in optical and magnetic attitude sensors, leading to better in-orbit simulation and validation on the ground. Overall, technology has not only improved test precision but also accelerated feedback loops, allowing for iterative development and early fault detection in complex attitude control systems.
The strategic and operational demands of modern warfare have amplified the importance of attitude testing, making it a critical area of investment and development in the defense landscape. One of the foremost drivers is the increasing deployment of autonomous and semi-autonomous systems that rely heavily on robust and accurate orientation control to function independently in dynamic and contested environments. UAVs, cruise missiles, and loitering munitions, for instance, must maintain a stable flight path, reorient swiftly, and adapt to changing mission parameters-functions that are highly dependent on precise attitude control systems tested rigorously beforehand. Another major driver is the rise of multi-domain operations, where joint missions across air, sea, land, space, and cyber domains require seamless interoperability of navigation and targeting systems, which in turn hinge on harmonized attitude data. The growing prevalence of hypersonic and space-based weapons introduces further complexity, as these systems demand advanced attitude control to maneuver at high velocities or in microgravity. Furthermore, stringent safety protocols and performance mandates from defense ministries require comprehensive attitude testing as part of system certification and acceptance trials. Export controls, especially for dual-use technology, also necessitate rigorous attitude performance validation, often under third-party or international standards. In addition, the evolving threat landscape-marked by countermeasures such as jamming, spoofing, and electronic interference-compels developers to stress-test attitude systems under degraded conditions to ensure operational resilience.
Globally, regional priorities and technological maturity levels are shaping diverse approaches to defense attitude testing. In North America, particularly the United States, attitude testing is a well-integrated component of defense R&D, with advanced simulation labs and aerospace test facilities supporting the development of high-performance guided munitions, space assets, and UAVs. U.S. defense agencies and OEMs invest heavily in real-time simulation rigs, inertial navigation validation systems, and flight dynamic modeling to support programs like hypersonic glide vehicles, missile defense interceptors, and orbital maneuvering units. Canada, with its aerospace heritage, supports attitude testing in the context of space surveillance, satellite missions, and defense-grade UAV platforms, often in collaboration with U.S. partners. In Europe, countries like Germany, France, and the UK emphasize attitude testing for NATO-integrated missile systems, future air combat platforms, and satellite-based communications. European initiatives focus on modular test environments and simulation capabilities that support cross-platform attitude control validation. Meanwhile, Asia-Pacific is emerging as a key growth area. China has rapidly scaled its capabilities for testing missile and space-borne platforms, emphasizing closed-loop simulations, real-time control testing, and redundancy verification in guidance systems. India, through ISRO and DRDO, has expanded its attitude testing infrastructure to support indigenous strategic missiles and space-based defense platforms. Japan and South Korea maintain specialized facilities for satellite and high-altitude reconnaissance vehicle attitude testing, with a strong focus on precision and miniaturization. In the Middle East, defense modernization initiatives in countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE are driving investments in simulation labs and testbeds for missile defense and drone programs, often through joint ventures with Western technology providers. Across all regions, the growing reliance on autonomous, networked, and space-enabled systems ensures that attitude testing remains a dynamic and high-priority field in defense R&D.
Russian forces are currently testing their new Molniya drones, which have been targeting Kharkiv in particular. This was revealed by Oleh Syniehubov, head of the Regional Military Administration (RMA), in a statement to News Live, as reported by Censor.NET. "Molniya-1 and Molniya-2 drones are being used. They are dangerous, and we are actively monitoring their presence. We believe the enemy is in the testing phase, as strikes on Kharkiv are occurring but not in large numbers. There are more frequent attacks using these 'lightning bolts' on Kupiansk and other settlements near the front line or close to the border. However, we're already seeing newer generations, which confirms the testing phase," he explained.
By Region
By Type
By Platform
By Component
The 10-year Global Attitude Testing Market in defense analysis would give a detailed overview of Global Attitude Testing Market in defense growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
The 10-year Global Attitude Testing Market in defense forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
The regional counter drone market trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.