
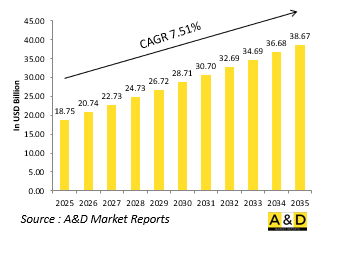
세계 네트워크 중심전 시장 규모는 2025년에 187억 5,000만 달러로 추정되며, 2035년까지 386억 7,000만 달러로 성장할 것으로 예측되고 있으며, 예측 기간인 2025-2035년 연간 평균 성장률(CAGR)은 7.51%에 다다를 전망입니다.
네트워크 중심전(NCW)은 전술적, 전략적 우위를 얻기 위해 정보의 우위를 활용하는 것을 중심으로 하는 군사 교리의 변혁적인 전환을 의미합니다. 센서, 통신 네트워크, 지휘 시스템, 전투 부대를 원활하게 통합하여 일관되고 즉각적인 실시간 작전 환경을 구축합니다. NCW의 핵심은 정보를 전투력으로 전환하는 것으로 군인, 의사결정자, 정보 자산을 영역 횡단적으로 연결하고, 상황 인식 강화, 작전 동기화, 의사결정 사이클의 고속화를 실현하는 것입니다.
기존의 지휘 통제 구조는 분산형 의사결정과 협조적인 대응을 가능하게 하는 디지털 방식으로 상호 연결된 시스템에 대체되고 있습니다. 이 프레임워크를 통해 군은 특히 역동적이고 복잡한 전투 지역에서 더 높은 민첩성, 정확성 및 적응성으로 활동할 수 있습니다. 네트워크 중심전은 공중과 사이버의 영역에 머무르지 않고 지상, 해상, 우주, 그리고 통합군의 환경에까지 확대되어 실시간으로 작전을 통합하여 전장의 역학을 재구성합니다. 위협이 혼재되어 있으며 분산되고 기술적으로 정교한 오늘날의 멀티도메인 분쟁에서는 정보 지배력을 확보하고 전력 강화를 가능하게 하기 위해 NCW가 필수적입니다. 실시간 UAV 피드에서 위성 통신 릴레이에 이르기까지 세계적인 방위 시장 지형은 동맹 유닛 간 정보 공유의 깊이와 속도에 따라 점점 더 정의되고 있습니다.
NCW를 지원하는 기술 환경은 급속히 진보하여 현대의 군이 작전을 계획 및 실행하는 방법을 근본적으로 바꾸고 있습니다. NCW의 핵심은 전술 데이터 링크, 위성 네트워크, 5G/6G 기능 등의 광대역 통신 인프라입니다. 이들은 지상 부대, 항공 자산 또는 지휘부 등 모든 네트워크의 모든 노드 간에 중단 없는 연결성을 보장합니다. 인공지능(AI)과 머신러닝(ML)은 NCW의 효율성을 높이는 데 중요한 역할을 합니다. AI 알고리즘은 방대한 데이터 세트를 실시간으로 처리하여 위협 식별, 전술적 대응 제안 또는 인적 개입을 최소화한 자산 배포 최적화를 수행할 수 있습니다. 예측 분석은 또한 더 나은 임무 계획과 위험 평가를 가능하게 하고, 지휘관이 전략적 결정에 자신감을 갖도록 합니다.
무인 차량, 원격 센서, 로봇 지원 유닛과 같은 자율 시스템의 성장은 네트워크화된 아키텍처에 대한 의존성을 더욱 강화하고 있습니다. 사이버 보안과 복원력도 NCW 시스템에 있어서 필수적인 요소가 되고 있습니다. 교리 전체가 데이터의 흐름과 디지털 연결에 의존하고 있기 때문에 통신 링크를 방어하여 데이터 침해, 방해 전파, 사이버 방해 행위로부터 보호하는 것이 가장 중요합니다. 그 때문에 양자 암호화, 블록체인 통신, 그리고 다계층 인증절차가 적극적으로 도입되고 있습니다.
또 하나의 중요한 기술적 진보는 웨어러블 전장 네트워크와 미래보병체계의 통합입니다 최신 보병체계는 현재 신체장착형 컴퓨터, 헤드업 디스플레이, 바이오 센서, 전술 무선 기능을 갖추고 있습니다.
NCW의 세계적인 채용과 확대를 뒷받침하는 것은 여러 핵이 되는 촉진요인입니다.
작전의 복잡화와 멀티도메인 전쟁에 의해 종래의 부대 구조는 유효성을 잃고 있습니다. 현대의 분쟁에서는 의사결정의 속도와 육상, 해상, 공중, 사이버, 우주의 각 영역에 걸친 제휴 능력이 매우 중요합니다. NCW는 이러한 통합 신속 작전을 가능하게 하며 기존의 느린 시스템을 사용하는 적에 대해 비대칭 우위를 제공합니다.
지정학적 불안정성과 동맹 관계의 변화도 세계의 방위 태세에 영향을 주고 있습니다.
AI, 클라우드 컴퓨팅, 에지 프로세싱, IoT 융합 등의 기술적 수렴을 통해 NCW에 필요한 인프라는 보다 접근하기 쉬우며 확장성이 높아지고 있습니다.
또한 반군 네트워크, 사이버 공격, 무인항공기와 같은 비대칭 및 하이브리드 위협으로 인해 NCW의 사용이 필요합니다. 전통적인 군과는 달리, 이러한 위협은 종종 분산적이며 기동성이 높습니다.
국방 현대화 프로그램은 세계적으로 디지털화와 연결성에 중점을 두고 있습니다.
마지막으로 연합군과 다국적군의 작전에 있어서의 상호운용성의 요건이 NCW 기술의 표준화와 채용을 촉진하고 있습니다.
미국은 NCW 능력의 개척자이며 지배적 국가입니다. 합동전영역지휘통제(Joint All-Domain Command and Control)와 같은 프로그램을 통해 육해공군, 해병대, 우주군 등 모든 부대를 통합하고 AI와 자율형 시스템으로 지원하는 통합 지휘계통을 구축함으로써 전쟁 방식을 변화시키고 있습니다. 또한 방어 태세를 강화하기 위해 디지털 지휘 능력을 추진하고 있습니다. NATO는 NCW를 집단 방어의 중요한 수단으로 받아들이고 있습니다. Krafte"와 영국의 "Land Environment Tactical Communication and Information Systems"(LE TacCIS)는 육상 부대를 디지털화하고 플러그 앤 플레이 지휘 환경을 구축하는 노력의 한 예입니다. 프랑스, 스웨덴, 폴란드도 방공, 국경 감시, 파병 작전에 NCW의 틀을 통합하고 있습니다.
중국은 "정보화"의 깃발 아래 네트워크 중심전 능력을 적극적으로 추진하고 있습니다. 인민해방군(PLA)은 우주, 사이버, 물리 작전을 일체화한 통합 지휘 네트워크 구축을 목표로 하고 있습니다. 일본과 한국은 C4ISR(지휘, 통제, 통신, 컴퓨터, 인텔리전스, 감시, 정찰) 인프라를 현대화하여 특히 지역의 긴장 속에서 신속한 데이터 공유와 실시간 위협에 대한 대응을 견고히 하고 있습니다. 호주는 향후 전력 컨셉의 일환으로 통합 전투 관리 시스템에 투자하고 있으며 원활한 통합 운영을 목표로 하고 있습니다. 사우디아라비아, 아랍에미리트(UAE), 카타르 등의 걸프 국가들은 국내 안보와 전력 투사를 모두 강화하기 위해 NCW 시스템을 빠르게 도입하고 있습니다. 이 지역의 조달 전략은 통합 방공 미사일 방어 시스템과 장갑 및 보병 부대의 전장 디지털화를 중시하고 있습니다. 이스라엘은 특히 센서 퓨전, 드론 연계, 사이버 대응 전장 인식에 있어서 NCW 배치의 리더로 자리잡고 있습니다.
아프리카에서의 NCW 도입은 최근에 시작되었지만 성장하고 있습니다. 남아프리카, 이집트, 나이지리아와 같은 국가들은 기본적인 네트워크 중심전 구성 요소를 채택하여 반군 활동과 국경 경비 활동을 조정합니다. 아프리카 대륙의 과제인 연결성이 낮은 인프라와 제한된 예산은 채택 속도를 늦추고 있습니다. 그러나 지원을 바탕으로 하는 현대화 프로그램과 지역 안보 이니셔티브을 통해 NCW 원칙을 일부 군부대에 도입하고 있습니다.
인도에서는 무인항공기와 미사일과 같은 선진 시스템의 도입에 미디어의 주목이 집중되어 있습니다. 하지만 육군이 20년 이상 요구해 온 종합적인 네트워크 중심전 능력에 대한 격차는 여전히 존재합니다.
본 보고서에서는 세계 네트워크 중심전 시장에 대해 조사했으며, 10년간의 부문별 시장 예측, 기술 동향, 기회 분석, 기업 프로파일, 국가별 데이터 등을 정리했습니다.
이 장에서는 향후 10년간의 네트워크 중심전 분석을 통해 네트워크 중심전의 성장, 변화 추세, 기술 채택의 개요, 전반적인 시장 매력에 대해 상세한 개요를 제공합니다.
이 부문에서는 이 시장에 영향을 미칠 것으로 예상되는 상위 10개 기술과 이러한 기술이 시장 전체에 미칠 수 있는 영향에 대해 설명합니다.
세계 네트워크 중심전 예측
이 시장의 10년간의 네트워크 중심전 예측은 위의 부문 전체에서 자세히 설명하고 있습니다.
지역 네트워크 중심전 동향과 예측
이 부문은 지역의 네트워크 중심전 동향, 촉진요인, 억제요인, 과제, 그리고 정치, 경제, 사회, 기술 등의 측면을 포괄하고 있습니다. 지역 분석의 마지막 단계에서는 주요 기업 프로파일, 공급업체 상황, 기업 벤치 마크 등에 대해 분석합니다.
북미
촉진요인, 억제요인, 과제
PEST
주요 기업
공급업체 티어 상황
기업 벤치마킹
유럽
중동
아시아태평양
남미
이 장에서는 시장 내 주요 방위 프로그램을 다루며 이 시장에서 발생하는 최신 소식과 특허에 대해서 설명하고, 국가 수준의 10년간 시장 예측과 시나리오 분석에 대해서도 설명합니다.
미국
방위 프로그램
최신 뉴스
특허
이 시장의 현재 기술 성숙도
캐나다
이탈리아
프랑스
독일
네덜란드
벨기에
스페인
스웨덴
그리스
호주
남아프리카
인도
중국
러시아
한국
일본
말레이시아
싱가포르
브라질
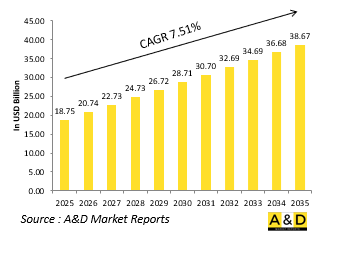
The Global Network Centric Warfare market is estimated at USD 18.75 billion in 2025, projected to grow to USD 38.67 billion by 2035 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 7.51% over the forecast period 2025-2035.
Network Centric Warfare (NCW) represents a transformative shift in military doctrine, centered on leveraging information superiority to gain a tactical and strategic advantage. It involves the seamless integration of sensors, communication networks, command systems, and combat units into a cohesive, responsive, and real-time operational environment. At its core, NCW is about turning information into combat power-connecting shooters, decision-makers, and intelligence assets across domains to achieve enhanced situational awareness, synchronized operations, and faster decision cycles.
Traditional command-and-control structures are being replaced by digitally interconnected systems that enable distributed decision-making and coordinated responses. This framework allows militaries to operate with greater agility, precision, and adaptability, particularly in dynamic and complex combat theaters. Network centric operations are not confined to air or cyber realms-they extend across ground, sea, space, and joint-forces environments, unifying efforts in real-time and reshaping battlefield dynamics. In today's multi-domain conflicts-where threats are hybrid, dispersed, and technologically sophisticated-NCW is critical for gaining information dominance and enabling force multiplication. From real-time UAV feeds to satellite communication relays, the global defense landscape is increasingly defined by the depth and speed of information sharing among allied units.
The technology landscape underpinning NCW has advanced rapidly, fundamentally altering how modern militaries plan and execute operations. At the heart of NCW are high-bandwidth communication infrastructures, including tactical data links, satellite networks, and 5G/6G capabilities. These ensure uninterrupted connectivity between all nodes in the network, whether ground troops, air assets, or command centers. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) play a significant role in enhancing the efficiency of NCW. AI algorithms can process massive datasets in real time, identifying threats, suggesting tactical responses, or optimizing asset deployment with minimal human intervention. Predictive analytics also enables better mission planning and risk assessment, giving commanders more confidence in their operational decisions.
The rise of autonomous systems-such as unmanned vehicles, remote sensors, and robotic support units-has further intensified reliance on networked architecture. These assets often operate semi-independently but remain tightly integrated within the command network, requiring robust and secure protocols to maintain synchronization and responsiveness. Cybersecurity and resilience have also become integral aspects of NCW systems. Since the entire doctrine depends on data flow and digital connectivity, defending communication links and protecting against data breaches, jamming, and cyber sabotage are paramount. As such, quantum encryption, blockchain-secured communications, and multi-layered authentication mechanisms are being actively developed and deployed.
Another key technological advancement is the integration of wearable battlefield networks and smart soldier systems. Modern infantry kits now include body-worn computers, heads-up displays, biosensors, and tactical radios-all of which feed into and extract data from the broader network. This creates a digitized warfighter, capable of interacting with drones, vehicles, and headquarters in real-time while remaining mobile and lethal.
Several core drivers are propelling the adoption and expansion of NCW capabilities on a global scale.
Operational complexity and multi-domain warfare have made traditional force structures less effective. In modern conflicts, the speed of decision-making and the ability to coordinate across land, sea, air, cyber, and space domains are crucial. NCW enables that kind of integrated, fast-paced operation, offering an asymmetric advantage over adversaries relying on slower, legacy systems.
Geopolitical instability and shifting alliances are also influencing the global defense posture. As nations face uncertain security environments, they are investing in NCW to boost their defense readiness and interoperability with allied forces. For instance, NATO's emphasis on joint operability and coordinated command systems has accelerated NCW adoption among member states.
Technological convergence-the blending of AI, cloud computing, edge processing, and IoT-has made the infrastructure required for NCW more accessible and scalable. Militaries are now able to build resilient, modular NCW frameworks using off-the-shelf technologies integrated with custom military-grade solutions, reducing cost and deployment time.
Asymmetric and hybrid threats, such as insurgent networks, cyberattacks, and drone swarms, further necessitate the use of NCW. Unlike conventional armies, these threats are often decentralized and mobile. Countering them requires the rapid dissemination of intelligence, flexible deployment strategies, and real-time threat visualization-all hallmarks of NCW.
Defense modernization programs globally are heavily focused on digitization and connectivity. Countries are launching NCW-centric initiatives that restructure command chains, update platforms with networking capabilities, and train forces to operate in a connected battlefield. Procurement priorities are shifting toward platforms and systems that can "plug into" these digital architectures seamlessly.
Lastly, interoperability requirements in coalition and multinational operations are driving standardization and adoption of NCW technologies. Whether in joint exercises or real-world missions, being able to share a common operational picture across forces is essential-and NCW provides the backbone for such synchronization.
The United States is the pioneer and dominant force in NCW capabilities. Through programs like Joint All-Domain Command and Control (JADC2), the U.S. Department of Defense is transforming how it fights wars by integrating all branches-Army, Navy, Air Force, Marines, and Space Force-into a unified command structure supported by AI and autonomous systems. Canada is similarly advancing its digital command capabilities to better coordinate joint operations and reinforce Arctic defense postures. NATO has embraced NCW as a critical enabler of collective defense. European nations are investing in secure, interoperable command platforms that can work across member states. Germany's "Digitale Krafte" and the UK's "Land Environment Tactical Communication and Information Systems" (LE TacCIS) are examples of efforts to digitize land forces and create plug-and-play command environments. France, Sweden, and Poland are also integrating NCW frameworks into air defense, border surveillance, and expeditionary operations.
China is aggressively advancing its network-centric capabilities under the banner of "informatization." The People's Liberation Army (PLA) aims to build integrated command networks that unify space, cyber, and kinetic operations. Japan and South Korea are modernizing their C4ISR (Command, Control, Communications, Computers, Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance) infrastructures to ensure rapid data sharing and real-time threat response, especially in the context of regional tensions. Australia is investing in integrated battle management systems as part of its future force initiatives, aiming for seamless joint-service operability. Gulf countries such as Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Qatar are rapidly adopting NCW systems to enhance both internal security and power projection. The region's procurement strategies emphasize integrated air and missile defense systems, as well as battlefield digitization for armored and infantry units. Israel remains a leader in NCW deployment, particularly in sensor fusion, drone coordination, and cyber-enabled battlefield awareness.
NCW implementation in Africa is still nascent but growing. Countries like South Africa, Egypt, and Nigeria are adopting basic network-centric components to coordinate counterinsurgency efforts and border patrol operations. The continent's challenges-ranging from low connectivity infrastructure to limited budget-slow down the pace of adoption. However, donor-backed modernization programs and regional security initiatives are introducing NCW principles into select military units.
In India, media attention has increasingly centered on the induction of advanced systems such as drones and missiles. However, significant capability gaps remain in public perception-such as the Indian Air Force's declining squadron strength, the Navy's shortage of submarines, and the delayed induction of the Army's Advanced Towed Artillery Gun System (ATAGS). One critical yet less visible gap that persists is the Army's long-standing requirement-spanning over two decades-for comprehensive Network Centric Warfare capabilities. Central to this is the implementation of an Integrated Battlefield Management System (BMS) for land forces, a need that continues to demand focused attention and resolution
Network centric warfare Report Definition
Network Centric Warfare Segmentation
By Region
By Type
By Platform
Network centric warfare Analysis for next 10 Years
The 10-year network centric warfare analysis would give a detailed overview of network centric warfare growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
Global Network centric warfare Forecast
The 10-year network centric warfare forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
Regional Network centric warfare Trends & Forecast
The regional network centric warfare trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
Country Analysis of Network centric warfare
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
Opportunity Matrix for Network centric warfare
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Expert Opinions on Network centric warfare Report
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.