
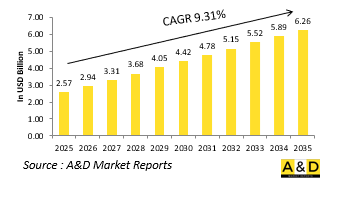
세계의 소형 UAV 시장 규모는 2025년에 25억 7,000만 달러로 추정됩니다. 2035년까지 62억 6,000만 달러로 성장할 것으로 예상되며, 예측 기간의 2025-2035년 연간 평균 성장률(CAGR)은 9.31%를 나타낼 전망입니다.

소형 UAV는 미니 드론이나 전술 드론이라고 불리는 것이 많아, 세계의 현대적인 군사 작전에 불가결한 것이 되고 있습니다. 통상, 날개 폭 3m 미만, 중량 150kg 미만의 UAV로 정의되는 이러한 플랫폼은 근거리 정찰, 감시, 목표 포착, 통신 중계, 심지어는 경전투의 역할을 위해서 설계되고 있습니다. 전략적 임무에 사용되는 대형 UAV와 달리, 소형 군사 UAV는 스피드, 스텔스성, 전개의 용이함이 중요한 전술적 환경이 뛰어납니다. 크고 다용도의 플랫폼에 대한 의존도를 높이고 있습니다. 그 저렴하고, 조작의 용이함, 적응성에 의해 통상 부대와 특수 작전 부대의 양쪽 모두에게 귀중한 툴이 되고 있습니다. 많은 지형, 밀집한 시가지, 원격지의 전장 등 대형 시스템에서는 효율적으로 운용할 수 없는 장소에서의 임무에 최적입니다.
기술의 진보는 군용 소형 UAV의 능력과 실용성을 대폭 향상시켰습니다. 가장 큰 변화를 가져온 것은 센서와 페이로드의 소형화입니다. 현재는 성능을 희생하지 않고 소형 UAV에 탑재할 수 있을 정도로 소형화되어 있습니다. 소형 UAV의 채용 방법을 재정의하고 있습니다. 고도의 네비게이션 알고리즘에 의해 GPS를 무시한 운용이 가능하게 되어, 전자적인 경쟁 환경에서는 극히 중요합니다. 또한 소형 UAV 그룹이 독립적으로 협력하고 적의 방어를 압도하고 집중 제어없이 광범위한 범위를 커버 할 수있는 그룹 알고리즘이 개발되었습니다.
배터리와 추진력 향상으로 내구성과 운영 범위가 향상되었습니다. 고밀도 리튬 유황 배터리, 하이브리드 추진 시스템, 심지어 태양 보조 설계를 채택하여 비행 시간은 이전 한계를 훨씬 넘어서고 있습니다. 이러한 기술 혁신을 통해 빈번한 재배치 없이 지속적인 모니터링을 유지하고 장기간의 임무를 지원할 수 있습니다. 전자전의 위험이 증가하고 있기 때문에 안전한 통신과 데이터 암호화가 중요해지고 있습니다. 최신 군용 소형 UAV의 대부분은 경쟁 전자기 환경에서의 내성을 보장하기 위해 현재 안티 재밍 기능과 주파수 호핑 기능을 갖추고 있습니다. 동시에, 온보드 데이터 처리는 많은 양의 데이터를 전송할 필요성을 줄이고 가로챌 위험을 줄입니다. 마지막으로 헤드업 디스플레이 및 전술 명령 네트워크와 같은 군인 시스템과의 통합으로 의사 결정과 반응 속도가 향상됩니다. 병사는 손목에 장착한 디바이스나 증강현실 인터페이스로부터 UAV를 기동·제어할 수 있게 되어, 움직이는 부대에 직접 리얼타임의 피드백을 제공하는 것으로, 이러한 드론을 원격 툴이라고 하는 것보다 전장의 팀 메이트와 같은 존재로 하고 있습니다.
몇 가지 중요한 요인들이 세계 군사 활동에서 소형 UAV 수요와 전개를 추진하고 있습니다. 소형 UAV는 숨겨진 위협 감지, 알려지지 않은 지형 매핑, 속도 및 스텔스 성이 최우선 되는 환경에서 정밀 타격 유도에 있어서 전술적 우위성을 제공합니다.예산 효율과 비용 대비 효과도 강력한 추진력입니다. 따라서 군사대국뿐만 아니라 개발도상국과 자원이 한정된 부대에서도 이용할 수 있습니다.
국경 경비와 대반란 작전도 도입에 영향을 미치고 있습니다. 비살상성 페이로드를 장비할 수 있기 때문에 교전을 수반하지 않는 억제에도 유효합니다. 또한 중요한 요인은 네트워크 중심 전쟁 능력에 대한 투자 증가입니다. 전 팀에 직접 데이터를 전송하는 능력으로 실시간 디지털 전장에서 중요한 노드가 되고 있습니다. 이에 가까운 위협의 대두에 의해 군는 전술적 ISR(인텔리전스, 감시, 정찰) 능력을 최저 레벨로 향상시킬 필요에 강요되고 있습니다.
세계의 군용 소형 UAV 채용은 지역에 따라 다르며 지정 학적 우선 사항, 군사 독트린, 기술 능력의 영향을 받고 있습니다. Hornet과 같은 플랫폼은 미군의 다양한 부문에서 폭넓게 사용되고 있습니다.특수 부대나 통상 부대와의 통합에 의해 이러한 시스템은 전술적 ISR이나 임무 지원의 정평이 되고 있습니다.
유럽에서는 특히 ISR 능력과 전장 네트워킹 강화를 요구하는 NATO 회원국들 사이에서 채용이 꾸준히 성장하고 있습니다. 그리고 독일의 Mikado 시리즈는 모듈식으로 병사가 운반할 수 있는 UAV를 개발하기 위한 국산화 노력의 일례입니다. 또한, 유럽 방위청은 공동 임무를 지원하기 위해, 무인기의 상호 운용성 기준을 중시하고 있습니다. 중국은 국내 사용과 수출 모두에서 소형 UAV 플릿을 급속히 확대하고 있습니다.
드론 기술 혁신의 세계 리더인 ideaForge Technology Limited는 이 회사의 SWITCH MINI UAV가 영광스러운 'Fit for Indian Military Use' 인증을 받은 최초의 유일한 소형 UAV가 되었다고 발표했습니다. UAV의 탁월한 성능, 품질, 신뢰성 외에도 인도군의 엄격한 운용 기준을 충족하는 능력을 평가한 것입니다.
미국 육군은 유타 주에 거주하는 드론 제조업체, Teal Drones에 시험 및 평가 프로세스를 거쳐 동사의 블랙 위도우 무인 항공기 수천대를 공급하는 계약을 체결했습니다.
본 보고서에서는 세계의 소형 UAV 시장에 대해 조사했으며, 10년간의 부문별 시장 예측, 기술 동향, 기회 분석, 기업 프로파일, 국가별 데이터 등을 정리했습니다.
지역별
유형별
용도별
이 장에서는 10년간의 소형 UAV 시장 분석을 통해 소형 UAV 시장의 성장, 변화하는 동향, 기술 채용 개요 및 시장 매력에 대한 자세한 개요를 제공합니다.
이 부문에서는 이 시장에 영향을 미칠 것으로 예상되는 상위 10개 기술과 이러한 기술이 시장 전체에 미칠 수 있는 영향에 대해 설명합니다.
이 시장의 향후 10년간의 소형 UAV 시장 예측은 위의 부문에 걸쳐 상세하게 설명됩니다.
이 부문에서는 지역별 소형 UAV 시장 동향, 성장 촉진요인, 성장 억제요인, 과제, 그리고 정치, 경제, 사회, 기술 등의 측면을 망라하고 있습니다. 또한 지역별 시장 예측과 시나리오 분석도 상세 지역 분석의 마지막은 주요 기업프로파일 링, 공급업체의 상황, 기업 벤치 마크를 포함하고 있습니다.
북미
성장 촉진요인, 성장 억제요인, 과제
PEST
주요 기업
공급업체 계층의 상황
기업 벤치마킹
유럽
중동
아시아태평양
남미
이 장에서는 이 시장에서 주요 방위 프로그램을 다루며 이 시장에서 신청된 최신 뉴스와 특허에 대해서도 설명하고, 국가 수준의 10년간 시장 예측과 시나리오 분석에 대해서도 설명합니다.
미국
방위 프로그램
최신 뉴스
특허
이 시장의 현재 기술 성숙도
캐나다
이탈리아
프랑스
독일
네덜란드
벨기에
스페인
스웨덴
그리스
호주
남아프리카
인도
중국
러시아
한국
일본
말레이시아
싱가포르
브라질
The Global Small UAV market is estimated at USD 2.57 billion in 2025, projected to grow to USD 6.26 billion by 2035 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 9.31% over the forecast period 2025-2035.
Small Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), often referred to as mini or tactical drones, have become integral to modern military operations across the globe. Defined typically as UAVs with a wingspan under 3 meters and weighing less than 150 kg, these platforms are designed for close-range reconnaissance, surveillance, target acquisition, communication relay, and even light combat roles. Unlike larger UAVs used for strategic missions, small military UAVs excel in tactical environments where speed, stealth, and ease of deployment are critical. The global military landscape is increasingly leaning on these compact, versatile platforms for frontline intelligence and rapid situational awareness. Their affordability, ease of operation, and adaptability make them valuable tools for both conventional forces and special operations units. Small UAVs can be launched by hand, catapult, or vertical take-off methods, making them ideal for missions in rugged terrain, dense urban zones, or remote battlefields where larger systems cannot operate efficiently. As the nature of warfare shifts toward mobility, urban engagement, and multi-domain operations, small UAVs are emerging as indispensable assets across land, sea, and air-based units.
Technological advancements have significantly elevated the capability and utility of small military UAVs. The most transformative impact has come from miniaturization of sensors and payloads. Electro-optical and infrared cameras, synthetic aperture radars, electronic warfare modules, and chemical sensors are now small enough to be carried by mini-UAVs without sacrificing performance. This allows troops to gather actionable intelligence in real time without revealing their position. Autonomy and artificial intelligence are also redefining how small UAVs are employed. Advanced navigation algorithms allow for GPS-denied operations, crucial in electronically contested environments. AI-enabled object recognition helps UAVs distinguish between civilians, vehicles, or weapons systems, enabling real-time threat identification. Furthermore, swarm algorithms are being developed to allow groups of small UAVs to coordinate independently, overwhelming enemy defenses and enabling large-area coverage without centralized control.
Battery and propulsion improvements are enhancing endurance and operational range. The adoption of high-density lithium-sulfur batteries, hybrid propulsion systems, and even solar-assisted designs have extended flight times well beyond earlier limits. These innovations make it possible to maintain persistent surveillance or support prolonged missions without frequent redeployment. Secure communications and data encryption have become critical due to the growing risk of electronic warfare. Many modern military small UAVs are now equipped with anti-jamming and frequency-hopping capabilities to ensure resilience in contested electromagnetic environments. In parallel, onboard data processing reduces the need to transmit large volumes of data, lowering the risk of interception. Finally, the integration with soldier systems-such as heads-up displays or tactical command networks-enhances decision-making and reaction speed. Troops can now launch and control UAVs from wrist-mounted devices or augmented reality interfaces, providing real-time feedback directly to units in motion, making these drones more like battlefield teammates than remote tools.
Several key factors are propelling the demand and deployment of small UAVs in military operations worldwide. Chief among them is the changing nature of warfare, which increasingly emphasizes rapid maneuvering, decentralized operations, and asymmetric threats. Small UAVs offer a tactical edge in detecting hidden threats, mapping unknown terrain, and guiding precision strikes in environments where speed and stealth are paramount. Budget efficiency and cost-effectiveness are strong drivers as well. Compared to larger UAVs or manned aircraft, small drones are significantly cheaper to procure, maintain, and operate. This makes them accessible not only to major military powers but also to developing countries or units with limited resources. Their reusability and low-risk deployment further strengthen their appeal in contested regions or surveillance missions.
Border security and counterinsurgency operations are also influencing adoption. Nations dealing with smuggling, terrorism, and cross-border incursions require persistent surveillance without escalating conflict. Small UAVs serve this role effectively, offering real-time monitoring capabilities while minimizing human risk. They can be equipped with non-lethal payloads, such as acoustic devices or illumination flares, making them useful for deterrence without engagement. Another crucial factor is increased investment in network-centric warfare capabilities. Small UAVs are being integrated into broader combat systems as remote sensors or forward observers. Their ability to transmit data directly to artillery units, airstrike coordinators, or cyber warfare teams makes them vital nodes in the real-time digital battlefield. The emphasis on multi-domain operations-from land and sea to cyber and space-is accelerating the need for flexible UAV platforms that can adapt and interface with various command systems. The rise of peer and near-peer threats is pushing militaries to improve their tactical ISR (intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance) capabilities at the lowest levels. In conflicts where air dominance is contested or denied, small UAVs provide critical local eyes and ears that do not rely on traditional air support or satellite assets, giving ground troops the situational awareness needed to survive and win.
The global adoption of small military UAVs varies by region, influenced by geopolitical priorities, military doctrine, and technological capacity. North America, particularly the United States, leads in the research, development, and operational use of military small UAVs. Platforms like the RQ-11 Raven, Puma, and Black Hornet are extensively used across various branches of the U.S. military. Integration with special forces and conventional units alike has made these systems a staple in tactical ISR and mission support. The U.S. is also at the forefront of swarm technology and AI-driven UAVs through DARPA and other military research initiatives.
Europe is witnessing steady growth in adoption, especially among NATO members seeking enhanced ISR capabilities and battlefield networking. Countries like the UK, France, and Germany are investing in indigenous UAV programs to reduce dependence on U.S. platforms. France's NX70 and Germany's Mikado series are examples of localized efforts to develop modular, soldier-portable UAVs. Additionally, the European Defence Agency has emphasized interoperability standards for drones to support joint missions. Asia-Pacific presents a highly dynamic landscape. China has rapidly expanded its small UAV fleet for both domestic use and export. Chinese manufacturers such as DJI and AVIC are supplying the People's Liberation Army with a wide variety of drones, including swarm-capable units and backpack-portable systems for frontline troops. India is also making significant progress with its DRDO-developed UAVs and increased procurement of small drones for counter-insurgency and border patrol roles. Countries like South Korea, Japan, and Australia are prioritizing drone integration into their defense doctrines to counter regional threats and bolster coastal defense.
ideaForge Technology Limited, a global leader in drone innovation, proudly announces that its SWITCH MINI UAV has become the first and only small unmanned aerial vehicle to receive the prestigious "Fit for Indian Military Use" certification. This recognition highlights the UAV's exceptional performance, quality, and reliability, as well as its ability to meet the stringent operational standards of the Indian armed forces. The certification, awarded following rigorous evaluations conducted by the Directorate General of Quality Assurance (DGQA), marks a significant milestone for the Indian drone industry. It also reinforces ideaForge's standing as a global frontrunner in dual-use drone technologies designed for both defense and civilian applications.
The U.S. Army has awarded a contract to Utah-based drone manufacturer Teal Drones to supply thousands of its Black Widow unmanned aerial vehicles, following a successful test and evaluation process. Teal Drones, headquartered in Salt Lake City, produces the UAVs locally and operates as a subsidiary of Red Cat Holdings Inc., which is based in Puerto Rico.
By Region
By Type
By Application
The 10-year small UAV market analysis would give a detailed overview of small UAV market growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
The 10-year small UAV market forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
The regional small UAV market trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.