
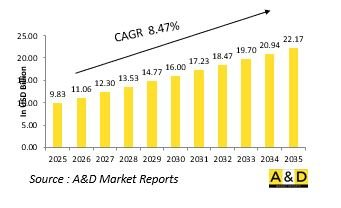
세계의 극초음속 미사일 시장 규모는 2025년 98억 3,000만 달러에서 예측 기간중 8.47%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)로 성장을 지속하여, 2035년에는 221억 7,000만 달러 규모로 성장할 것으로 예측됩니다.
국방 분야의 극초음속 미사일 시장은 현대전에서 가장 혁신적인 영역 중 하나로 빠르게 부상하고 있으며, 전략적 억제력과 공격 능력의 균형을 재정의하고 있습니다. 극초음속 미사일은 매우 빠른 속도로 비행하면서 높은 기동성을 유지하기 때문에 기존 방공 시스템을 회피하면서 고정밀 공격을 할 수 있습니다. 각국 국방 당국은 이러한 무기 시스템을 억제 및 전력 투사의 핵심 자산으로 간주하고 있습니다. 극초음속 미사일은 변화하는 위협에 대한 신속한 대응과 경고 시간을 최소화한 전략적 무기 투사를 가능하게 합니다. 현재 시장에서는 국방기관, 항공우주기업, 연구기관 간 설계, 추진, 유도 시스템의 공동 개발이 빠르게 진행되고 있습니다. 각국이 기술 우위를 확보하기 위해 경쟁하는 가운데, 극초음속 무기는 차세대 전쟁 독트린과 통합방위 전략의 핵심 요소로 떠오르고 있습니다.
기술의 발전은 극초음속 미사일의 속도, 정확도, 생존성을 형성하는 원동력이 되고 있습니다. 특히 스크램제트, 하이브리드 엔진 등 추진기술의 발전으로 극고도에서 지속적인 극초음속 비행이 가능해졌습니다. 또한 고온, 고압에 견딜 수 있는 첨단 소재를 채택하여 기체의 구조적 강도와 공기역학적 효율을 크게 향상시켰습니다. 또한 위성통신, AI 제어, 고도 알고리즘을 이용한 유도 및 항법 기술의 발전으로 이동 목표에 대해서도 높은 정확도를 유지하면서 동적으로 기동할 수 있는 능력을 획득하고 있습니다. 센서 융합 및 적응형 타겟팅 기술은 적대적인 환경에서 공격력을 더욱 향상시키고 있습니다. 또한, 고도의 지휘통제 네트워크와의 통합을 통해 실시간 임무 수정이 가능합니다. 이러한 기술적 혁신을 통해 극초음속 무기는 작전 운용의 유연성과 활용성을 획기적으로 확대하여 미래 타격 및 방어 시스템의 핵심으로 자리매김하고 있습니다.
극초음속 미사일 시장의 성장을 견인하는 것은 세계 방위 경쟁의 격화와 전략적 우위 확보에 대한 절박한 필요성입니다. 각국은 억지력 강화와 새로운 위협에 대한 신속하고 정밀한 대응 능력을 확보하기 위해 극초음속 무기 개발을 최우선 과제로 삼고 있습니다. 기존 미사일 방어 시스템으로는 극초음속 무기의 요격이 어렵기 때문에 각국은 공격형과 요격형 양면의 극초음속 프로그램에 대한 투자를 강화하고 있습니다. 또한, 장거리 정밀 공격 능력과 시간 의존성이 높은 표적 공격에 대한 수요는 극초음속 미사일 도입을 더욱 부추기고 있습니다. 국방 현대화 정책과 지정학적 갈등의 격화도 각국 정부에 자국 개발의 가속화를 촉구하고 있습니다. 또한, 공동 시험 프로그램 및 민관 협력은 추진, 열 제어 및 유도 기술 분야의 혁신을 촉진하고 있습니다. 결론적으로, 전략적 긴박감과 기술 혁신에 대한 야망은 이 시장의 성장을 뒷받침하는 두 가지 주요 원동력입니다.
세계의 극초음속 미사일 시장을 조사했으며, 시장 배경, 시장 영향요인 분석, 시장 규모 추이 및 예측, 각종 부문별/지역별 상세 분석 등의 정보를 정리하여 전해드립니다.
지역별
제품별
가이던스별
조사 내용 : 시장 동향, 성장 촉진요인 및 억제요인, 과제, PEST 분석, 시장 예측, 시나리오 분석, 주요 기업 개요, 공급업체 상황, 기업 벤치마킹
북미
성장 촉진요인 및 억제요인, 과제
PEST 분석
주요 기업
공급업체 상황
기업 벤치마킹
유럽
중동
아시아태평양
남미
미국
방위 프로그램
최신 뉴스
특허
이 시장에서의 현재 기술 성숙도
캐나다
이탈리아
프랑스
독일
네덜란드
벨기에
스페인
스웨덴
그리스
호주
남아프리카공화국
인도
중국
러시아
한국
일본
말레이시아
싱가포르
브라질
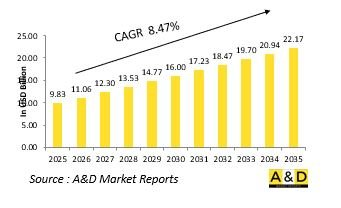
The Global Hypersonic Missiles market is estimated at USD 9.83 billion in 2025, projected to grow to USD 22.17 billion by 2035 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 8.47% over the forecast period 2025-2035.
The defense hypersonic missiles market is emerging as one of the most transformative domains in modern warfare, redefining the balance of strategic deterrence and offensive capabilities. Hypersonic missiles travel at extreme speeds while maintaining high maneuverability, allowing them to evade existing air defense systems and strike with precision. Defense forces across the world view these systems as crucial assets for both deterrence and power projection. They offer the ability to respond rapidly to evolving threats and deliver strategic payloads with minimal warning time. The market is witnessing rapid collaboration between defense agencies, aerospace companies, and research institutions to advance design, propulsion, and guidance systems. As nations compete to establish technological superiority, hypersonic weapons are becoming central to next-generation warfare doctrines and integrated defense strategies.
Technological progress has been the driving force behind the evolution of hypersonic missiles, shaping their speed, precision, and survivability. Advances in propulsion systems, particularly scramjet and hybrid engines, have enabled sustained hypersonic flight at extreme altitudes. Cutting-edge materials capable of withstanding intense heat and pressure have improved structural integrity and aerodynamic efficiency. Guidance and navigation technologies using advanced algorithms, satellite communication, and AI-based control systems allow these missiles to maneuver dynamically while maintaining accuracy against moving targets. Sensor fusion and adaptive targeting further enhance their lethality in contested environments. Additionally, integration with advanced command and control networks allows real-time mission adjustments. These technological breakthroughs collectively enhance the operational versatility of hypersonic weapons, positioning them as the cornerstone of future strike and defense systems.
The growth of the hypersonic missiles market is driven by escalating global defense competition and the need for strategic advantage in contested domains. Nations are prioritizing hypersonic capabilities to strengthen deterrence and ensure rapid, precise responses to emerging threats. The inadequacy of current missile defense systems to intercept hypersonic threats has intensified investments in both offensive and counter-hypersonic programs. The pursuit of long-range precision strike capabilities and time-sensitive targeting further supports the adoption of hypersonic weapons. Defense modernization initiatives, coupled with increasing geopolitical rivalries, are motivating governments to accelerate indigenous research and development efforts. Collaborative testing programs and public-private partnerships are also fueling innovation in propulsion, thermal management, and guidance technologies. Overall, strategic urgency and technological ambition are the key forces propelling this market's expansion.
Regional developments in the defense hypersonic missiles market reflect a global race for technological supremacy and deterrence capability. In North America, research and deployment efforts focus on achieving operational readiness and integrating hypersonic systems into multi-domain command structures. Europe is investing in cooperative research programs to strengthen regional defense autonomy and reduce reliance on external technologies. The Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a dynamic hub for hypersonic innovation, driven by regional tensions and extensive defense modernization programs. Middle Eastern countries are showing growing interest in these systems to enhance strategic defense layers and counter high-speed threats. Emerging defense markets in Latin America and Africa are monitoring global developments, exploring partnerships to gain access to early-stage hypersonic technologies. Across all regions, hypersonic weapons are reshaping national security priorities and driving a new era of competitive defense innovation.
Lockheed Martin has received a $1 billion contract modification from the U.S. Department of Defense to continue supporting the U.S. Navy's Conventional Prompt Strike (CPS) hypersonic weapons program.
The contract includes activities such as program management, engineering development, systems integration, procurement of long-lead materials, and the development of specialized tools and equipment. Work will take place across several Lockheed Martin facilities in the U.S., primarily in Denver, Colorado (49%), Huntsville, Alabama (35%), Sunnyvale, California (5%), Titusville, Florida (2%), and other locations covering the remaining 9%. The project is expected to run until August 31, 2028.
The CPS program is a joint Army-Navy initiative aimed at developing a common hypersonic weapon system featuring a shared glide body and missile design. The Army's version, called the Long-Range Hypersonic Weapon (LRHW) or "Dark Eagle," will be launched from mobile ground platforms, while the Navy's CPS system will be sea-based, integrated into surface ships and submarines.
By Region
By Product
By Guidance
The 10-year Hypersonic Missiles Market analysis would give a detailed overview of Hypersonic Missiles Market growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
The 10-year hypersonic missiles market forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
The regional hypersonic missiles market trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.